Pregnancy and Joint Pain
Why does joint pain occur during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, your body goes through many changes. The hormone relaxin makes your joints and ligaments looser to prepare for childbirth. This can make joints less stable and more painful. Added weight and changes in posture also put extra strain on your joints.
How common is joint pain in pregnancy in India?
Joint pain during pregnancy is very common. Globally, around 50-70% of pregnant women experience it, especially in the back and hips. In India, factors like less exercise and cultural practices may make it even more common.
Which joints are most affected?
- Lower back: Many women (up to 70%) feel back pain because of the growing belly and posture changes.
- Pelvis: The sacroiliac and pubic joints loosen due to relaxin, causing pain in 20-30% of pregnant women.
- Knees and ankles: Extra body weight can strain these joints.
- Wrists: Fluid retention can cause carpal tunnel syndrome, leading to wrist pain in 2-31% of women.
- Elbow: Tennis Elbow too is relatively common during Pregnancy causing pain in elbow.
Why does back pain happen during pregnancy?
Back pain is caused by:
- Posture changes as your belly grows.
- Weak abdominal muscles.
- Looser ligaments due to hormones like relaxin.
- Long periods of standing or wearing improper shoes.
What does relaxin do, and how does it cause joint pain?
Relaxin helps your body get ready for childbirth by loosening ligaments and joints. While necessary, it can make other joints unstable, leading to pain, especially in the pelvis and lower back.
How can you treat joint pain during pregnancy?
Here are safe ways to manage joint pain:
- Exercise: Light activities like walking, swimming, and yoga strengthen your muscles and reduce pain.
- Stretching: Gentle stretches for your back, hips, and legs help improve flexibility.
- Hot or cold packs: Use these to relieve pain and swelling.
- Good posture: Stand straight and wear supportive shoes.
- Paracetamol: Safe for occasional use, but always check with your doctor.
- Calcium and Vitamin D3: These strengthen bones and reduce pain caused by deficiencies. Pregnant women need 1000 mg of calcium and 600 IU of Vitamin D daily.
Why should you avoid painkillers like ibuprofen?
Painkillers like ibuprofen are not safe during pregnancy. They can harm the baby’s heart and cause delivery complications. Always talk to your doctor before taking any medication.
How do calcium and Vitamin D3 help with joint pain?
Calcium and Vitamin D3 are important for strong bones. Pregnant women need more of these nutrients, and a lack can cause joint pain. Supplements may be recommended if your diet doesn’t provide enough.
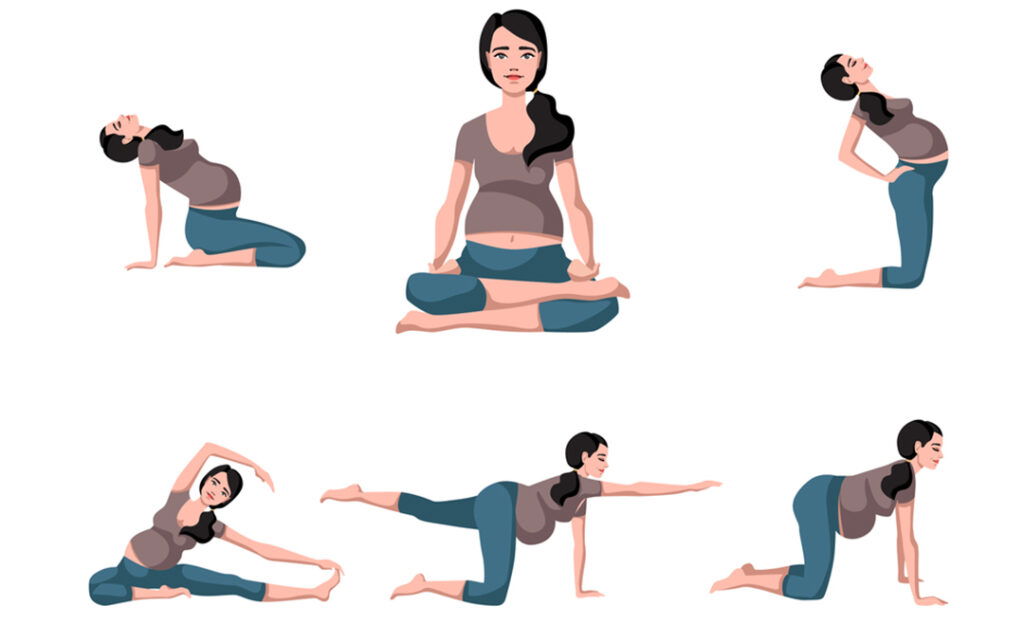
What exercises can help with joint pain?
Safe exercises include:
- Pelvic tilts: Strengthen your back and abdominal muscles.
- Cat-cow stretch: Loosens the lower back.
- Knee-to-chest stretch: Relieves pelvic pressure.
- Swimming: Takes pressure off your joints while strengthening muscles. Always check with a physiotherapist or prenatal specialist for guidance.
Can your diet help with joint pain?
Yes. Eating foods rich in calcium (like milk, yogurt, and greens) and Vitamin D (like fortified foods and getting sunlight) supports joint and bone health. Omega-3 fatty acids from fish or supplements may also reduce inflammation.
What role does hydration play in managing joint pain?
Staying hydrated is very important during pregnancy. Water helps keep your joints lubricated, which reduces stiffness and discomfort. Proper hydration also prevents muscle cramps and supports overall joint health. Dehydration can make joint pain worse, so aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water daily unless your doctor advises otherwise.
How does weight gain during pregnancy affect joint pain?
Weight gain during pregnancy puts extra pressure on your joints, especially in the lower back, knees, and ankles. This added stress can cause discomfort and inflammation. Gaining weight within the recommended range (11-16 kg for most women) helps reduce the strain on your joints and lowers the risk of long-term joint issues. The Extra Weight than the expected gain may not be ideal for your joints.
Common questions about pregnancy joint pain:
- Is joint pain normal after delivery?
- Yes, it usually goes away within a few weeks as your hormones return to normal.
- Can I use a support belt?
- Yes, maternity belts like (https://amzn.to/49MODnM) can reduce pelvic and back pain.
- Will the pain stop after pregnancy?
- Most women feel better after giving birth as weight decreases and ligaments tighten.
When should you see a doctor?
Visit your doctor if:
- Pain is severe or doesn’t go away.
- A joint is swollen, red, or warm.
- You feel numbness, tingling, or have trouble walking.