Rheumatoid Arthritis and Pregnancy
RA is a disease that is not only is for lifelong but also one of the most disabling conditions for patients, especially for young couples planning for parenthood.
It affects women three times more than men and that too mainly in their reproductive age.
Hence, this blog deals with the current management guidelines of RA for Pregnant Patients. Hopefully it will be valuable for both Doctors and Patients.
Will my Child too have RA?
Sadly, there are three times more chances from the general population of the Child suffering from RA and hence whenever the child suffers from any joint pain should be immediately checked up by a Doctor treating RA.
Does the disease decrease during Pregnancy?
Earlier it was thought in 75% of People disease activity decreases during pregnancy, Sadly newer studies confirmed that 20%-40% of Patients achieve remission (i.e. Decrease in disease symptoms) by Third Trimester.
20% of Pregnant Patients may have Worse or Moderate to High disease activity.
What will be the Disease course during Pregnancy?
DAS 28-CRP without Global Health assessment is the most preferred tool to measure disease activity.
Earlier it was thought in 75% of People disease activity decreases during pregnancy, Sadly newer studies confirmed that 20%-40% of Patients achieve remission (i.e. Decrease in disease symptoms) by Third Trimester.
20% of People may have Worse or Moderate to High disease activity.
Women with RF Negative are more likely to have fewer symptoms during Pregnancy.
What are the Pregnancy Outcomes?
- Increased risk of Pre-term birth.
- Some studies showed a risk of low birth weight
- No risk of congenital abnormality.
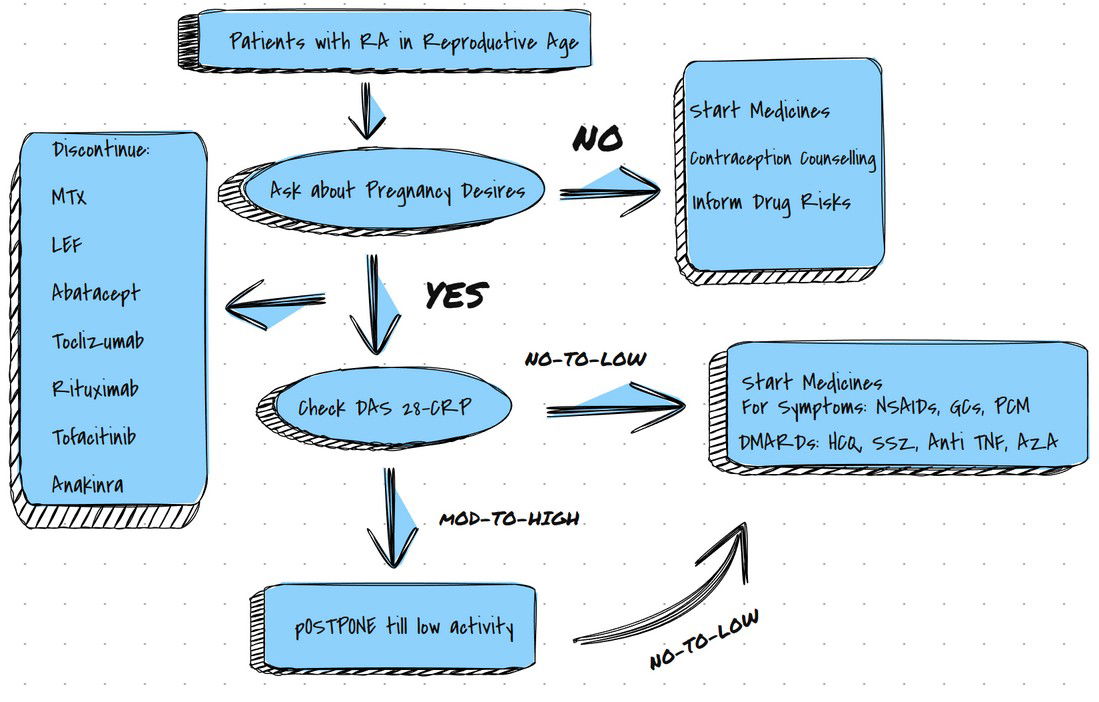
What are the recommendations regarding drugs?
1. NSAIDS:
Some studies show an increased risk of Abortion if used for more than a week.
Though a recent large prospective study shows no association.
No association with a congenital abnormality or premature birth or LBW.
Exception, Ibuprofen (Caused LBW when used in 2nd trimester)
NSAIDs increase the risk of premature closure of the Ductus Arteriosus and hence better not to use in the Third trimester.
2. Steroids (Glucorticoids):
One of the Most used drugs during pregnancy.
May or Most likely cause delivery before 37 weeks.
Conflicting data regarding Miscarriage/fetal deaths with one study showed no difference and another demonstrated higher occurrence.
No major congenital anomalies were noted with the use of GCs, however, the patient should be informed about the small but increased risk of oral clefts, if GC is used in 1st trimester.
Methotrexate: (Cat X)
Absolutely Contraindicated.
Causes spontaneous abortions,
MTX Embryopathy ( Heart, CNS, and skeleton)
Some case reports showed a low dose of MTX showed no side effects but No Dose till now can be defined as safe.
If Accidentally exposed to MTX, better to counsel the patient with Observational Data.
The largest dataset is from OTIS ( Organization of Teratology Information Services and European Network of Teratology Information Services).
Post-conception exposure has more risk of spontaneous abortion than preconception exposure.
Systemic review in 2009, 101 cases received MTX in 1st trimester, half resulted in Live Birth with no MTX embryopathy.
Women must be Counseled about Contraception if MTX is Advised.
Hydroxychloroquine: (Cat C)
Can safely be prescribed during Pregnancy.
No Spontaneous abortions, Fetal deaths, Premature births or Congenital defects
Sulfasalazine: (Cat B)
Can safely be prescribed during Pregnancy.
No Spontaneous abortions, Fetal deaths, Premature births or Congenital defects
Leflunomide: (Cat X)
Avoided in women planning Pregnancy.
A study by OTIS Collaborative research group, 64 females were exposed to LEF
The majority underwent a cholestyramine washout procedure ( to remove LEF from the system), 87.5 % had a live birth, 7.8% had Spontaneous abortion, and 1,6% had an elective abortion.
No LBW, No major structural abnormalities, except 3 defects,
- Occult spinal dysraphism,
- Unilateral ureteropelvic junction obstruction,
- Microcephaly.
Azathioprine: (Cat D)
Data taken from patients on Aza for IBD shows no major congenital defects or LBW.
Still considered as Cat D.
TNF Therapy: (Cat B)
Exposure linked to VACTERL.
41 Children showed 61 anomalies when had exposure to Etanercept or infliximab.
Only 1 had VACTERL, the rest all with one anomaly from VACTERL.
In a recent study, as per the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics registered 118 of 130 pregnancies exposed to anti-TNF the following congenital manifestations were noted:
- CDH (Congenital Dislocation of Hip
- Pyloric Stenosis
- Winking jaw syndrome
- Strawberry birthmark.
Other Studies:
- Israeli Teratology Information Service: No congenital anomalies seen
- PIANO: No congenital anomalies seen
- European Network of Teratology Information Services: 5% of pregnancies had birth defects.
- TREAT registry: 142 pregnancies, 92.4% had healthy babies.
- OTIS RA pregnancy project: No congenital anomalies seen
- TNF Inhibitors: No increased risk of spontaneous abortions.
Premature delivery has contrasting answers.
Infants may be more prone to infections.
Abatacept: (Cat C)
Attempt to conception: 14 weeks after the last dose.
151 pregnancies were exposed: only 86 had live births.
Multiple congenital anomalies are seen.
Rituximab: (Cat C)
Attempt to conception: 12 months after last dose.
153 pregnancies exposed had 59% live births. 24% of them were premature. with many child hematological abnormalities.
Anakinra: (Cat B)
Very little information is available.
Tocilizumab: (Cat C)
33 pregnancies were exposed, and 11 had term deliveries.
Tofacitinib: (Cat C)
No published data.
So what to advise a patient with RA and Unplanned Pregnancy?
Individualized discussion.
Risk of drugs with complications to be explained by using Data.
MTX and LEF to be STOPPED.
If on LEF, Recommended receiving cholestyramine to eliminate the drug.8gm thrice daily for 11 days, followed by plasma level of LEV evaluation with a goal of <0.02mg/Lt on two occasions separated by 2 weeks.
RA and Pregnancy and a FLARE?
Corticosteroids, with if possible Intra-articular mode.
NSAIDs (But caution in the third trimester)
Can I Breastfeed?
The decision must be taken after discussion regarding the wish of the Mother and the health benefits of breastfeeding, the Disease activity of RA, and the need for Medications.
In a study, Third trimester to 6 months postpartum: 1st time breastfeeding women at 6 months postpartum had the worst pain experience.
For acute flare: Prednisolone is the best Option.( Prednisolone levels in breast milk is 5%-25% of serum level, and hence child absorbs 0.1% of that dose, it's insignificant as endogenous production is much higher)
NSAIDs: (Ibuprofen, diclofenac, Indomethacin, Naproxen, and Piroxicam) are allowed as per the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Ibuprofen the lowest transfer rate to Infants also has a short half-life.
HCQ: Safest DMARD. Only 0.06-0.2mg/kg/day detectable in milk.
SULPHASALAZINE: No increase in serum values of children, Relatively safe to use.In a case report, a child developed bloody diarrhea, hence infants to be monitored for diarrhea.AAP recommends caution in Premature children, a child with G6PD Deficiency, or those with Jaundice.
AZA: Very low amount was noted in breast milk. Long-term study too did not find any harm.
MTX: TO BE AVOIDED.
LEF: No data available, hence TO BE AVOIDED.
BIOLOGICS: No data available for recommendations.
What about a Male patient with RA who wants to start a family?
RA in fathers is not associated with poor outcomes in the child.
MTX: Wait for 3 months after stopping MTX to attempt to conceive.
(Spermatogenic cycle is of 74 days)
however recent study, MTX exposed fathers did not increase major birth defects or abortions, or LBW.
SULPHASALAZINE: Associated with decreased sperm count, motility, and abnormal sperm morphology.
If a male patient has difficulty, with fertility, Sulphasalazine can be put on hold.
AZA: not associated with poor outcome.
LEF: Limited dataT
NF inhibitors: Conflicting data, but overall outcome is Positive.
Rituximab: Limited information.